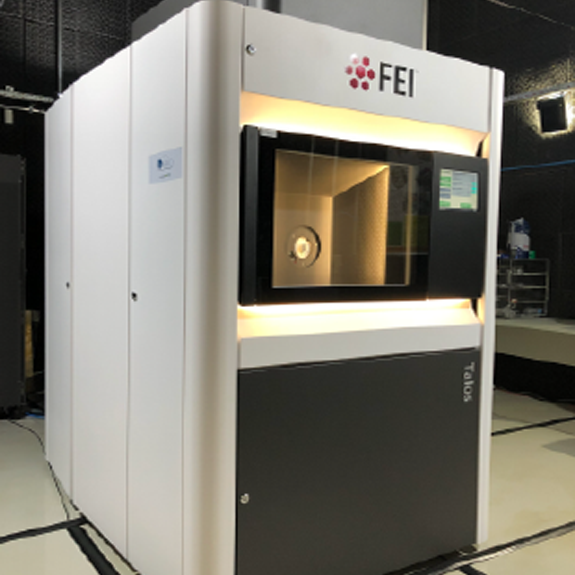
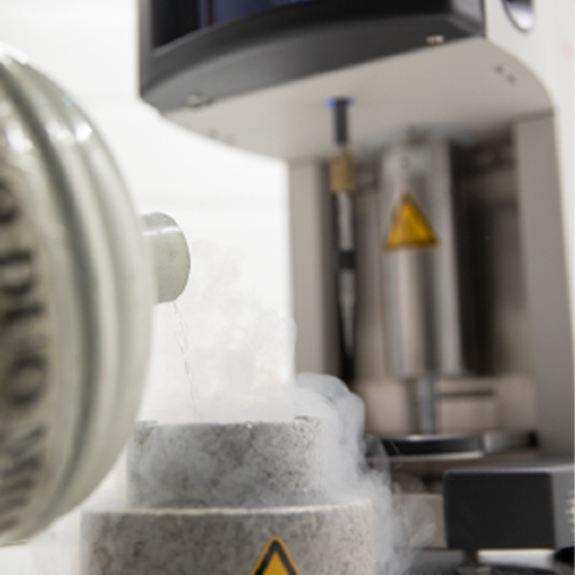
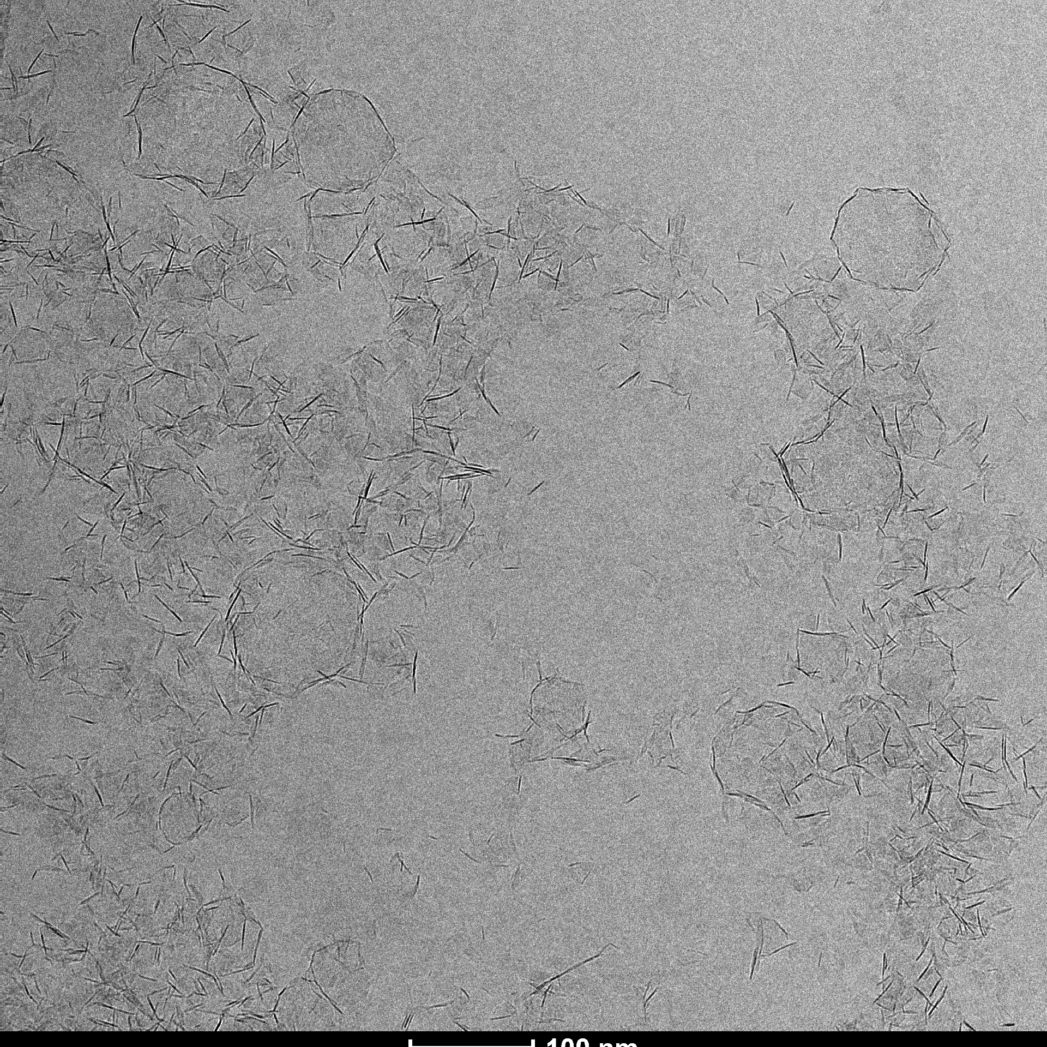
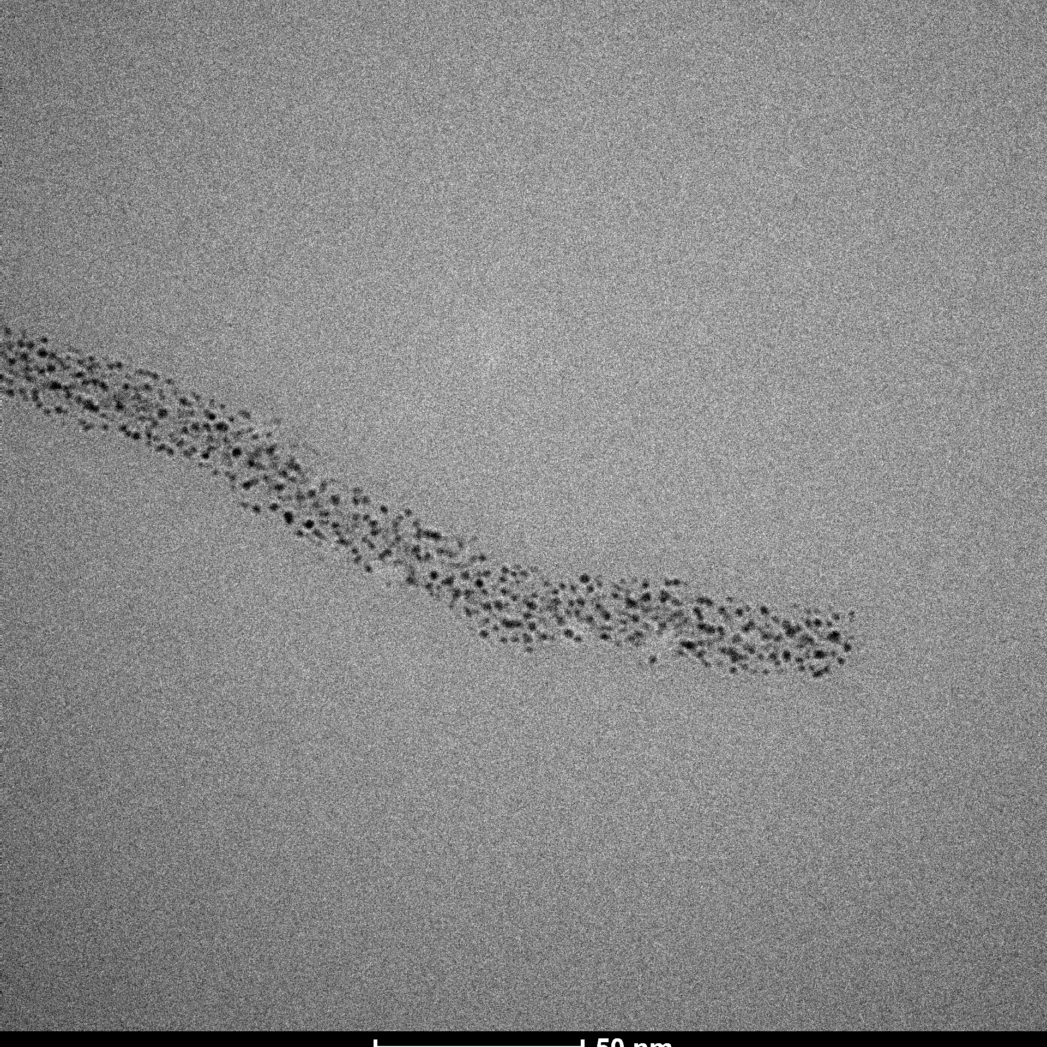
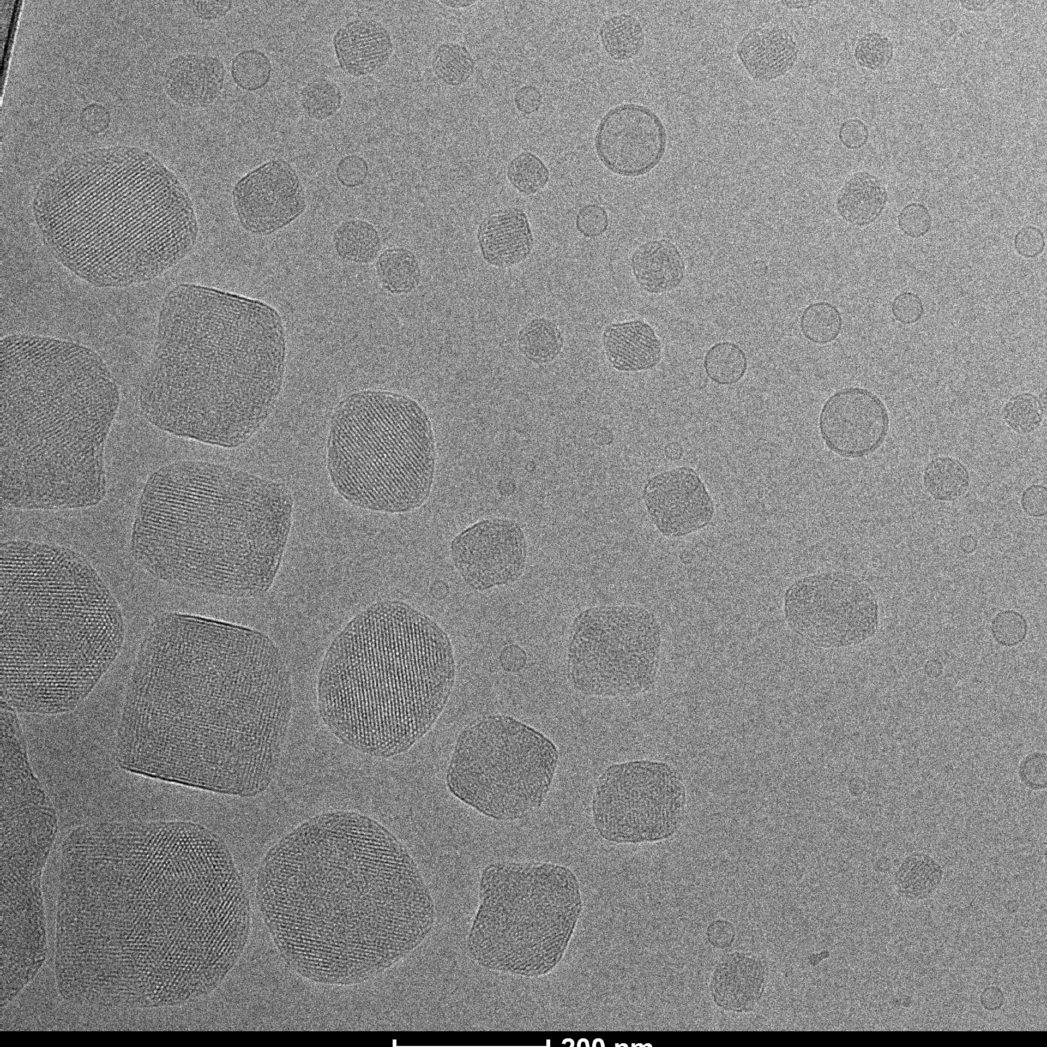
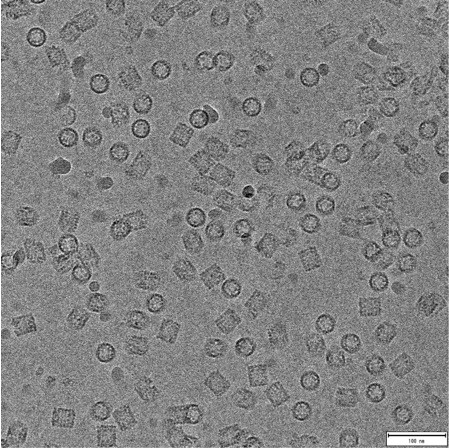
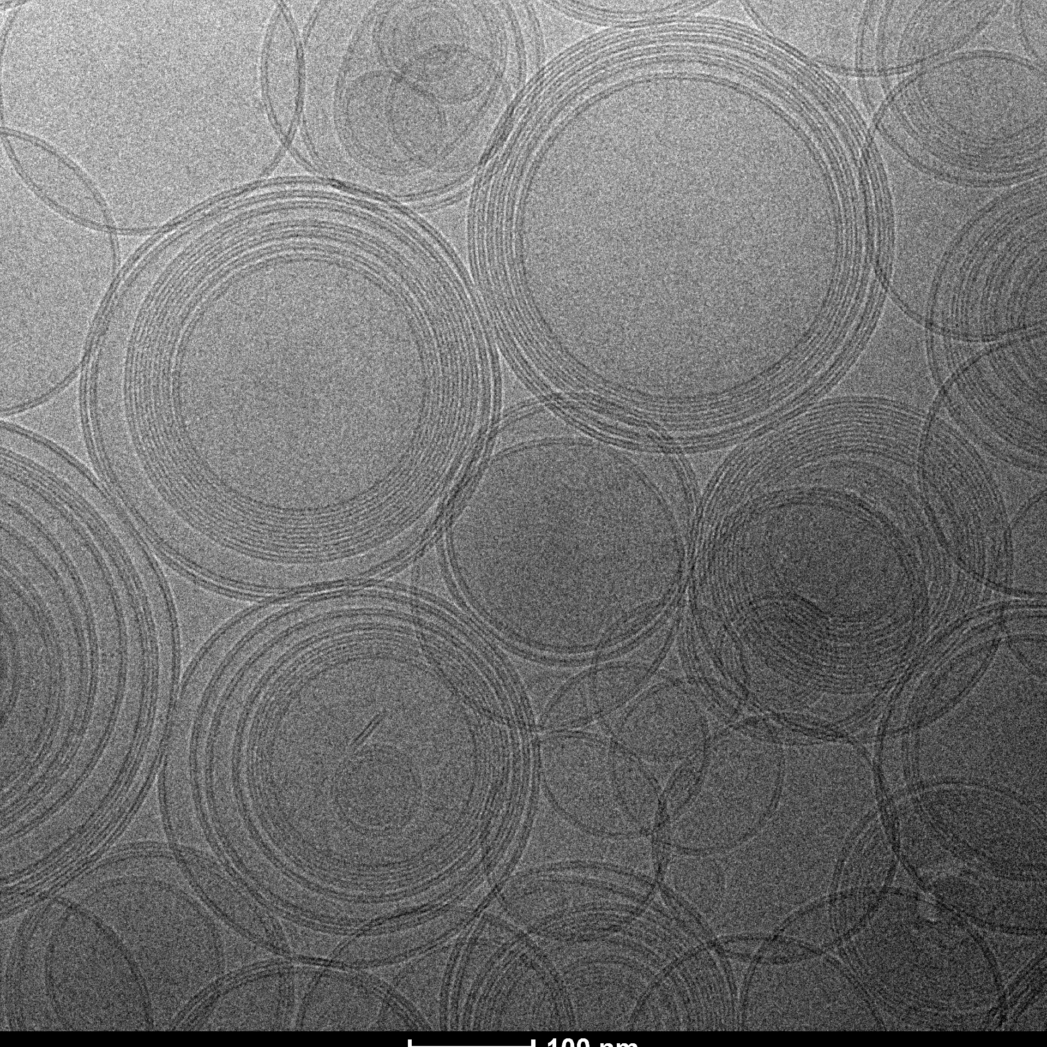
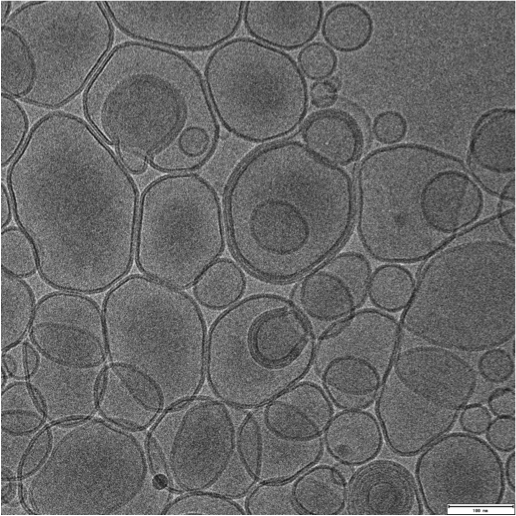
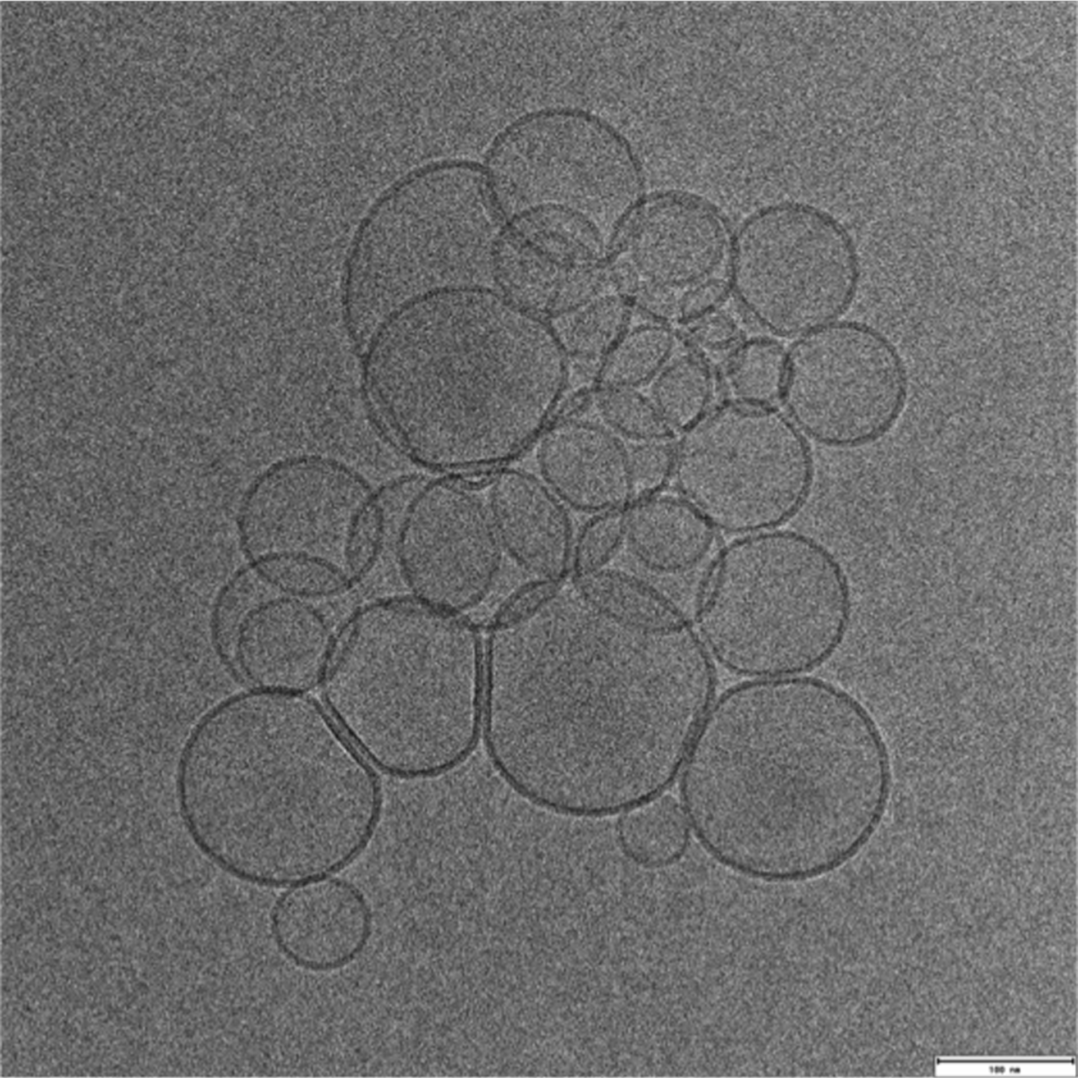
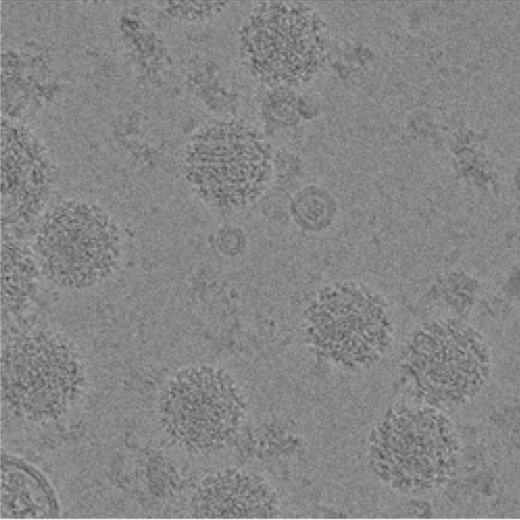
Transmission Electron Cryomicroscopy (Cryo-EM) is widely used for the observation of a variety of systems, from soft materials to biomolecules. Sample preparation is performed with its rapid freezing, which preserves the native state. Data collection is performed on different equipment. Soft materials, especially colloidal systems, can be directly observed as if they were in suspension, under low dose conditions, with high contrast and minimal damage to the sample. Biomolecules can have their structural information obtained in high resolution, using the analysis of isolated particles, accompanied by data collection in state-of-the-art equipment.
Electron cryomicroscopy in structural biology:
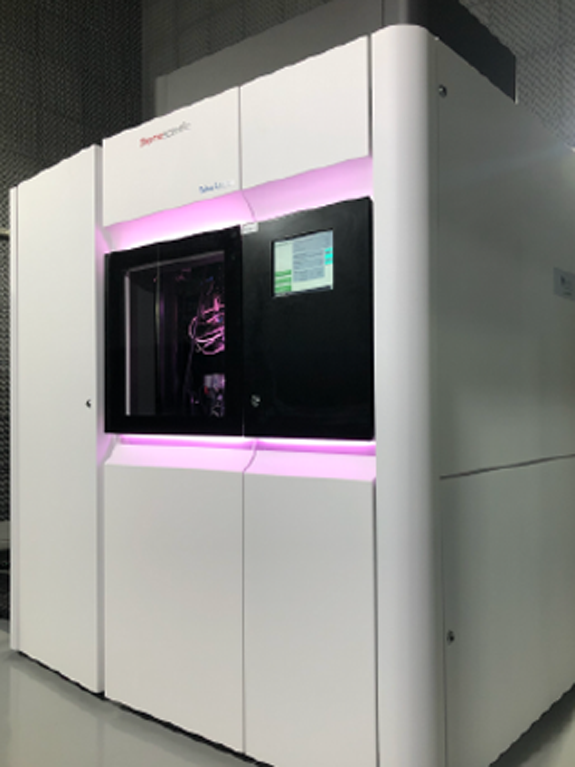
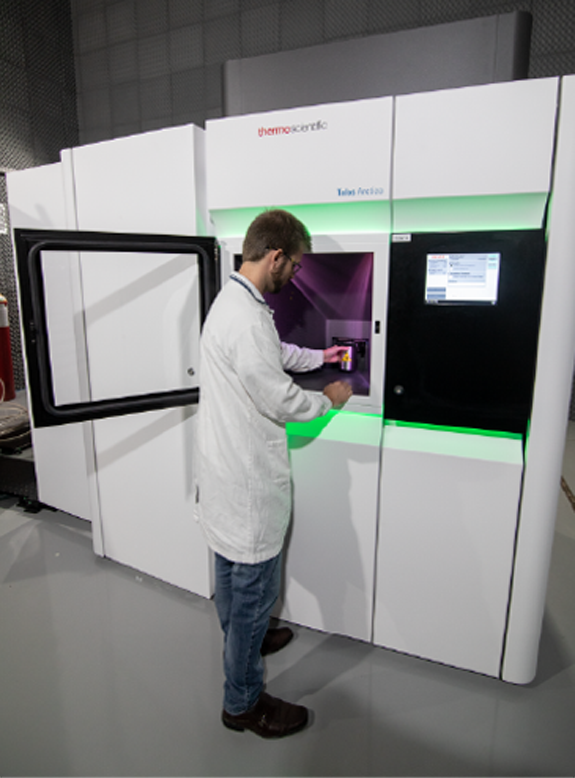
Cryo-ME is a powerful technique to investigate the structure of biomolecules. The rapid immersion method for vitrifying samples preserves the native structure of the particles which, together with the use of state-of-the-art microscopes and detectors, allows access to high resolution information in three-dimensional structures. LNNano has four transmission electronic cryomicroscopes, two of them fully equipped to participate in structural biology projects, with direct electron detectors, energy filter and “phase-plate”, operating at 200kV and 300kV. The sample preparation laboratories have automatic preparation systems and are equipped to support all necessary activities in sample preparation, including an NB-2 room.
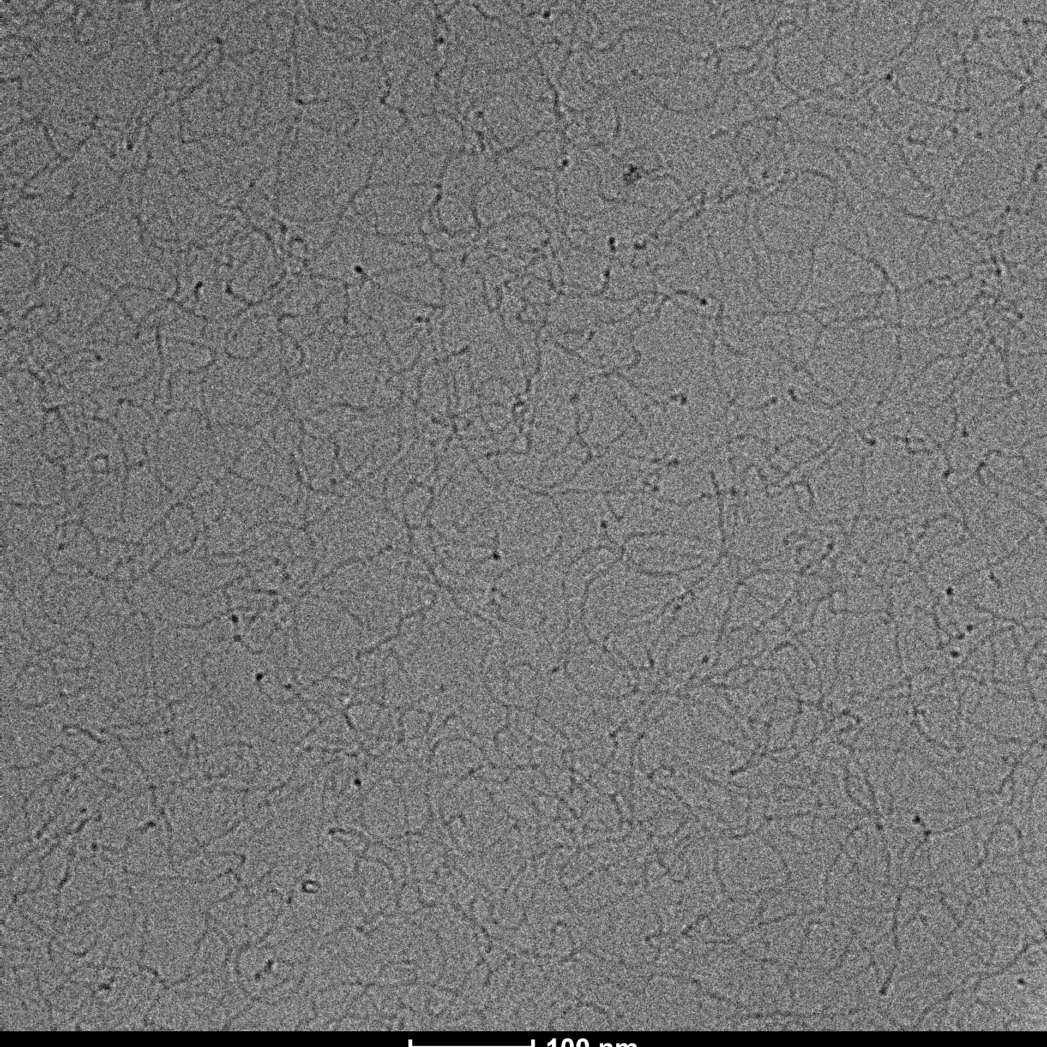
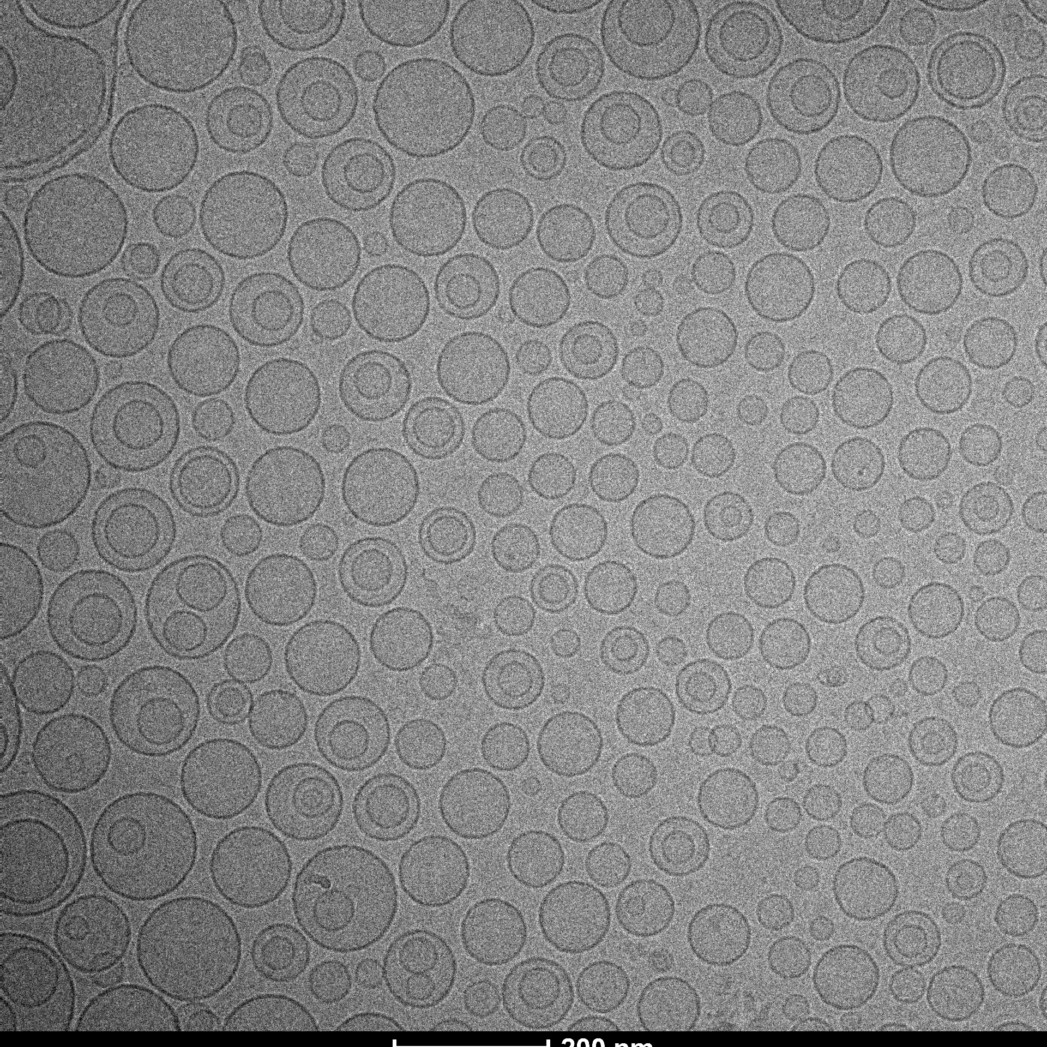
Electron Cryomicroscopy of Soft Materials:
Using Cryo-ME for sensitive materials and soft materials allows you to understand its structure, minimizing the effects of radiation damage and artifacts caused by drying during sample preparation. At LNNano’s facilities, users have different equipment for data collection, operating at 80kV, 200kV and 300kV, and equipped with low-dose cameras and direct electron detectors. This ensures that each project is supported with a suitable setup to achieve its goals.
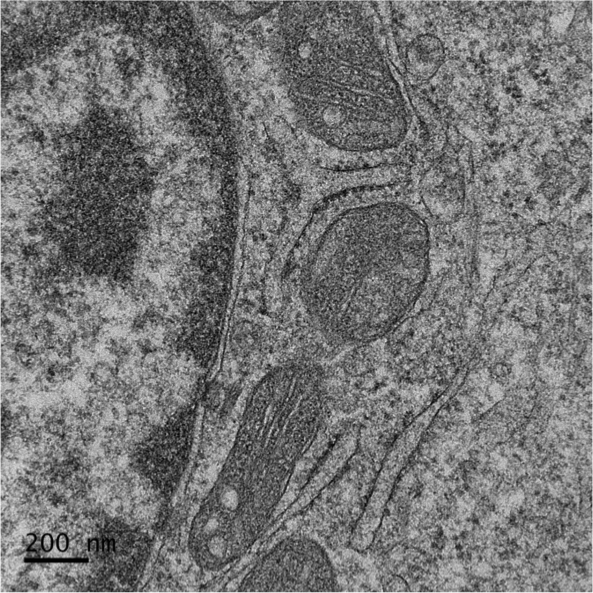
Electron Microscopy of counterstained samples
In addition to the use of cryomicroscopy, which allows direct observation of hydrated samples, contrast techniques can be used for analyzes at room temperature. These techniques can be applied to soft materials, cells, tissues and biological macromolecules. This analysis allows the observation of morphological characteristics, such as size, shape and aspect ratio. In the case of macromolecules, negative contrasting also allows obtaining low-resolution three-dimensional structural information.